The Student Startup & Innovation Policy
Government of Gujarat has developed a policy for providing assistance to Startups/ Innovation. Under this scheme, any individual/ group of individuals having innovative idea/ Concept will be eligible and/ or Universities/ education institutions, Incubation Centre/ PSUs/ R&D Institutions/ Private and other establishments will be eligible as an institution to support and mentor to innovators as approved by Committee. Startup in an economy’s technology sectors is an important indicator of technological performance for several reasons.
Gujarat Commerce College is always inquisitive to adopt innovative ideas of our glittering stars. All the students belong to the institute is suggested to apply for SSIP to have bright future. Here the detailed information is given according to the guidelines of Government of Gujarat.
Statistics deals with the collection, description, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. Statistics can be used to describe a particular data set (termed descriptive statistics) as well as to draw conclusions about the population from a particular data set (termed inferential statistics).
Key Objectives
The Student Startup & Innovation Policy of Government of Gujarat aims to create an integrated, state-wide, university-based innovation ecosystem to support innovations and ideas of young students and provide a conductive environment for optimum harnessing of their creative pursuit.
Developing student centric Innovation and Preincubation Ecosystem for Students (IPIES)
Creating environment for creativity to flourish and an end-to-end support system in educational institutions to allow ample support to ideas for better execution
Build internal capacity of educational institutions and key components of the innovation ecosystem to enable deployed processes to make sustainable impact at scale
Create pathways for mind to market by harnessing and handholding projects/ research/ innovation/ ideas of students in Gujarat
Creating and facilitating sectorial and regional innovation efforts in state around educational institutions
Create a common platform to showcase, support and upscale innovations for motivating stakeholders as well as for an opportunity to create value for money and value for many
Leverage public system initiatives at state and central level, academia, industries and by other ecosystem stakeholders / domain experts and institutions to make an inclusive effort
Key Goals
Empower all universities to set-up and execute the broad agenda of innovation and preincubation
Aim to create an environment that converts at least 1% graduates into job creators by innovation and allied means
Support at least 1,000 student-led innovations per year and aim to file 1000 patents from universities in the state every year
Harness 500 student startups in the next 5 years, and upscale
Empower universities and educational institutes to build a robust Innovation and Preincubation support systems within
Create incentives, awards, appreciations and benchmarks for innovation and student startups and associated efforts at all layers
Build capacity for at least 200 educational institutes in the state in the next five years, to have a robust preincubation support for student / alumni startups and Innovations
Undertake strategic interventions to empower all universities in the state to develop full-fledged preincubation ecosystem in the next 5 years
Ensure that the innovation processes link academia, society and SMEs through systematic ways so that students and faculty solve their challenges and create further entrepreneurial opportunities
Role of Stakeholders
Government: Mandate, support, facilitate, integrate and scale
Academic stakeholders: Deploy agenda within, quality assurance, create end-to-end support systems, and codification
Non-academic, industry and other ecosystem stakeholders: Mentoring, market access, and domain knowledge
In synchronisation with various central efforts like the Make In India, Startup India, Atal Innovation Mission, National Innovation Council etc., the Government of Gujarat has taken some concrete steps to support creativity, innovation and entrepreneurship.
POLICY INTERVENTIONS UNDERTAKEN BY GUJARAT FOR INNOVATION AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP
In 2013, the State Innovation Council was constituted under the Chairmanship of Chief Secretary and the ambit of the Department of Science and Technology to set an agenda of innovation for the state at macro level.
Subsequently, as a part of the 2015 Industrial Policy, an ‘Assistance Scheme for Startups and Innovations’ was launched by the Department of Industries and Mines to provide seed funding support to early stage startups.
In June 2016, the Department of Science and Technology of the state released the Electronics & IT/ITeS Startup Policy for supporting incubation infrastructure and allied support links, for ICT startups.
Innovation and entrepreneurship are not only confined to formal sectors and initiatives like the Gujarat Grassroots Innovation and Augmentation Network (GIAN) have created support systems to help the innovations in the informal sector in the state.
More than 10 incubators supported by Department of Science & Technology, Government of India, exist in the state and a few more are supported by central agencies such as DeiTy, DBT and MSME department.
Furthermore, iCreate is a public funded incubator established by the state Government.
THE SIGNIFICANCE OF UNIVERSITIES AND EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTES IN GUJARAT’S STARTUP ECOSYSTEM
Ahmedabad has the highest number of DST (Govt. of India) approved Technology Business Incubators (TBIs) – 10 – in any city. 8 out of these 10 are a part of academic institutions.
Out of the 20 Nodal Institutions (NIs) under the Startup Assistance Scheme of Gujarat Industrial Policy 2015, 18 are academic institutions.
The supply side of the innovation and startup value chain of Gujarat ecosystem is deeply rooted around research, project, and innovation activities across universities in Gujarat.
Gujarat took the first ever student startup initiative in the country at Gujarat Technological University which was later on scaled across universities in Andhra Pradesh and Kerala.
Nearly 200 student startups initiate across universities in Gujarat every year.
AICTE, under the ambit of the HRD Ministry, Government of India, is launching its own Startup Policy catering to technical institutes across the country including the institutes in Gujarat.
The existing massive pool of faculty members, researchers and research ecosystem, and common facilities are avenues for new ideas to get nourished in university system itself before young innovators have to approach external support in order to become a full-fledged startup.
The national Startup India action plan aims to create support for three layers: a) student startups / university innovation-based enterprises, b) existing startups in the country that exist at the post-incubation stage, and c) top, growth-stage startups that need regulatory and allied supports.
The Innovation and Preincubation Ecosystem Support (IPIES) Policy of Gujarat shall cater to the first layer of student startups and innovation ecosystem, and create base-level interventions to support the Gujarat startup ecosystem at all the layers.
NEED FOR CREATING END-TO-END SUPPORT FOR INNOVATIONS VIA EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTES
A progressive innovation and startup ecosystem comprises of several key components, mainly a vibrant academia led innovation, preincubation, incubation, acceleration, access to seed, angel and venture capital funding, market access, practical regulatory support, ease of doing business and growth and upscaling environment with government’s ownership to drive the agenda.
Interventions like the state’s assistance scheme for startups and innovations shall attain its optimum efficiency when a quality pool of innovations and early stage startups emerge from the ecosystem of Gujarat every year.
Gujarat has systematically built systems such as Gujarat Venture Fund Limited (GVFL), assistance scheme for startups, state-funded incubation facilities, such as iCreate, annual platform to showcase and discourse, etc.
While the existing support links are well positioned to help startups with funding, there is a wide-gap in the innovation development and preincubation phase.
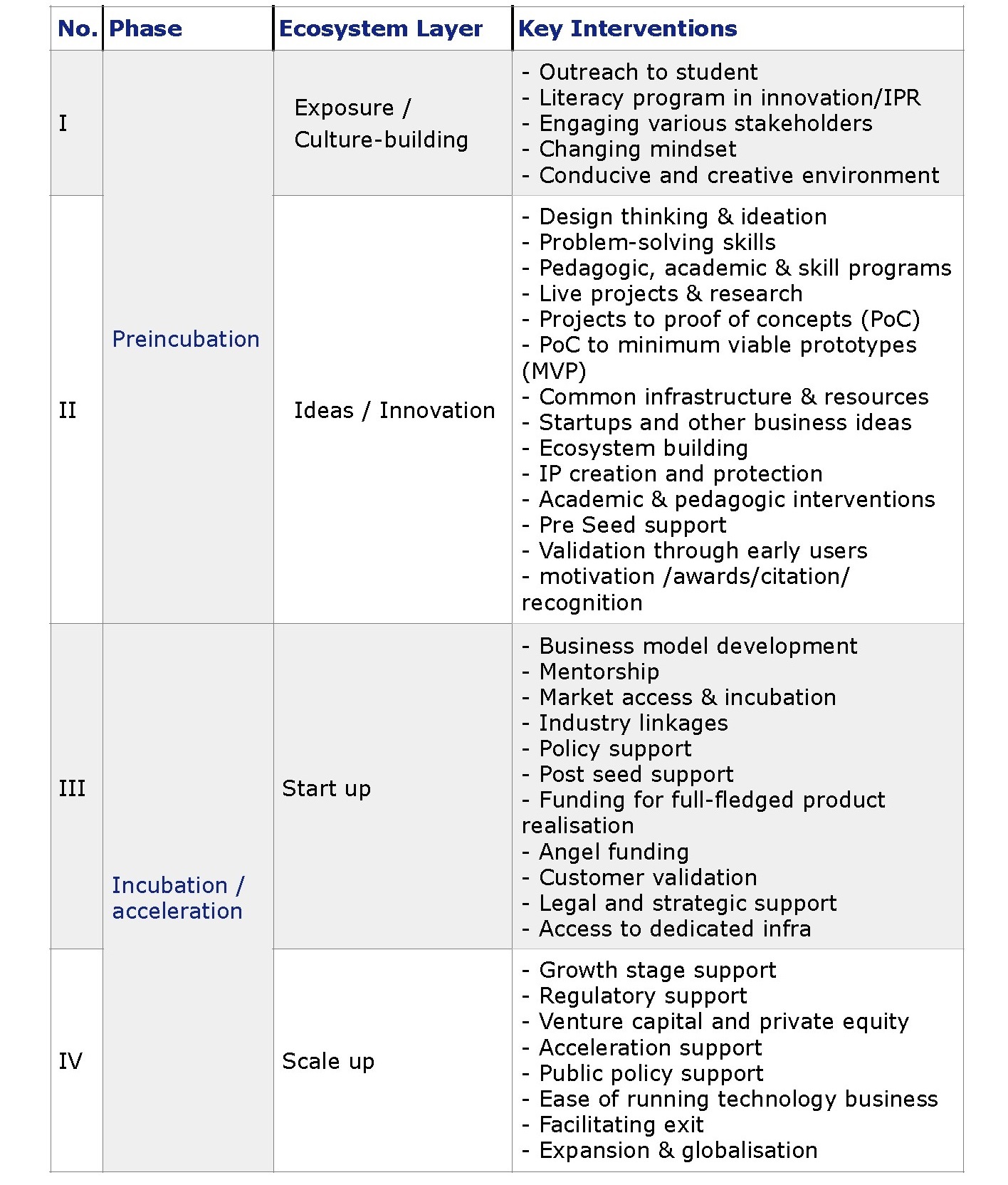
Also, as most of the progressive startup ecosystems in the world have witnessed an active role of local academia and students, the key missing link is the holistic innovation pre-startup and innovation ecosystem development across academia and allied stakeholders, which this policy aims to fill.
The Student Startup & Innovation Policy hence aims at ensuring that the students across all educational institutes of Gujarat get a conductive environment to solve problems and create ideas and opportunities. This policy addresses the need of creating a strong pipeline of innovations out of research and allied efforts across institutes, helping students convert ideas into opportunities, that later can be supported as startups through various existing institutional mechanisms.
The policy creates an innovation pyramid with lateral linkages as well as in-house support and adds on to the facilities already available.
Startup:
Startup is an entity that develops a business model based on either product innovation or service innovation and makes it scalable and replicable so as to be self-reliant. Startup may also be an entity that satisfies the requirements of the Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP),Government of India, notification dated 17.02.2016 as specified in the G.S.R. 180 (E).
Out of the 20 Nodal Institutions (NIs) under the Startup Assistance Scheme of Gujarat Industrial Policy 2015, 18 are academic institutions.
The supply side of the innovation and startup value chain of Gujarat ecosystem is deeply rooted around research, project, and innovation activities across universities in Gujarat.
Gujarat took the first ever student startup initiative in the country at Gujarat Technological University which was later on scaled across universities in Andhra Pradesh and Kerala.
Nearly 200 student startups initiate across universities in Gujarat every year.
AICTE, under the ambit of the HRD Ministry, Government of India, is launching its own Startup Policy catering to technical institutes across the country including the institutes in Gujarat.
The existing massive pool of faculty members, researchers and research ecosystem, and common facilities are avenues for new ideas to get nourished in university system itself before young innovators have to approach external support in order to become a full-fledged startup.
The national Startup India action plan aims to create support for three layers: a) student startups / university innovation-based enterprises, b) existing startups in the country that exist at the post-incubation stage, and c) top, growth-stage startups that need regulatory and allied supports.
The Innovation and Preincubation Ecosystem Support (IPIES) Policy of Gujarat shall cater to the first layer of student startups and innovation ecosystem, and create base-level interventions to support the Gujarat startup ecosystem at all the layers.
STARTUP DEFINITION (AS DEFINED BY DIPP)
- (Source: https://www.startupindia.gov.in/)
STARTUP MEANS AN ENTITY, INCORPORATED OR REGISTERED IN INDIA :
Upto a period of seven years from the date of incorporation/registration or upto ten years in case of Startups in Biotechnology sector
As a private limited company or registered as a partnership firm or a limited liability partnership
With an annual turnover not exceeding Rs. 25 crore for any of the financial years since incorporation/registration
Working towards innovation, development or improvement of products or processes or services, or if it is a scalable business model with a high potential of employment generation or wealth creation Provided that an entity formed by splitting up or reconstruction of an existing business shall not be considered a ‘Startup’.
AN ENTITY SHALL CEASE TO BE A STARTUP:
On completion of seven years from the date of its incorporation/registration, ten years in case of Startups in Biotechnology sector, or
If its turnover for any previous year exceeds Rs. 25 crore
https://www.startupindia.gov.in/uploads/notifications/notification_StartupNotification11April2018.pdf
STUDENT STARTUP:
Student Startup is any student-led innovation based startup that has been founded by the efforts of one or more student(s) and / or alumni (not more than 5 years from graduation), from any university / educational institute in the state, with or without the help of faculty guides and external support agents. Recently, AICTE has developed a national roadmap for student startup support system.
Conceptually, any innovation implies substantial improvement in the ways of doing things, producing goods or providing services. It may involve a new use of an existing resource or producing or delivering existing goods or services through new methods or new instruments/materials.
INNOVATION DEFINITION:
(Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Innovation)
Innovation can be defined simply as a “new idea, device or method”.[1] However, innovation is often also viewed[by whom?] as the application of better solutions that meet new requirements, unarticulated needs, or existing market needs.[2] Such innovation takes place through the provision of more-effective products, processes, services, technologies, or business models that are made available to markets, governments and society. The term “innovation” can be defined[by whom?] as something original and more effective and, as a consequence, new, that “breaks into” the market or society.[3] Innovation is related to, but not the same as, invention,[4] as innovation is more apt to involve the practical implementation of an invention (i.e. new/improved ability) to make a meaningful impact in the market or society,[5] and not all innovations require an invention. Innovation often[quantify] manifests itself via the engineering process, when the problem being solved is of a technical or scientific nature.

Benefit to Student Innovators & Start-ups
Exposure: SSIP is going to provide detailed exposure to all students, early stage innovators and allied stakeholders through regular programs, workshops, conferences and seminars. Each SSIP grantee university, institute has been given specific mandate and resources to facilitate large scale exposure programs keeping early stage student innovators in mind.
Capacity building: SSIP is allocating dedicated resources for capacity building of innovators and student start-ups involving domain experts of national and international repute.
Support for Prototyping: SSIP has created mechanism through which students, innovators, start-ups can be given up to 2 lac INR for developing prototype. Through State SSIP grant committee deserving teams can even fetch grant more than 2 lac per project as per the need. SSIP is one of the very few scheme through which innovators are being supported through seed level grant at nascent stage.
Support for IPR: Through SSIP, innovators can avail average 25 lac INR grant for domestic IPR filing. SSIP also mandate to support student innovators for IPR protection beyond India and give incentives for them.
Pre Incubation Support: SSIP has short listed various colleges and universities and given grant to create a robust pre incubation process and infrastructure in their respective campuses. Innovators from respective campuses and around the region can fetch benefits through these nodal centers of SSSIP. Innovators can approach to any of the SSIP grantee through web portal and approach to avail SSIP benefits.
Co working and Pre incubation Support at I Hub: SSIP is setting up a state level innovation hub which will be linked with all university level innovation & start-up centers. In this center early stage student innovators and start-ups can benefit of coworking space, mentoring, access to various programs and allied benefits. SSIP is going to host different sectoral incubators in this hub so that innovators and start-ups across domain and stage of their innovation, enterprise can benefit from this.
Regional Innovation & Start-up Centers: SSIP will extend facilities to innovators and students of even remote places through its 4 regional centers at Ahmedabad, Surat, and Vadodara & Rajkot. Institutes & their students in the nearby region can benefit hugely benefit out of these centers. Makers lab and similar prototyping facilities will be built in these centers to let innovators access to world class facilities.
